Urban Heat Island Cool Roofs Remote Sensing

Heat islands can be defined for different layers of the urban atmosphere and for various surfaces and even the subsurface oke 1995 voogt oke 1997 it is important to distinguish between these different heat islands as their underlying mechanisms are different oke 1982 roth et al 1989 unless otherwise indicated an urban heat island refers to the excess warmth of the urban atmosphere.
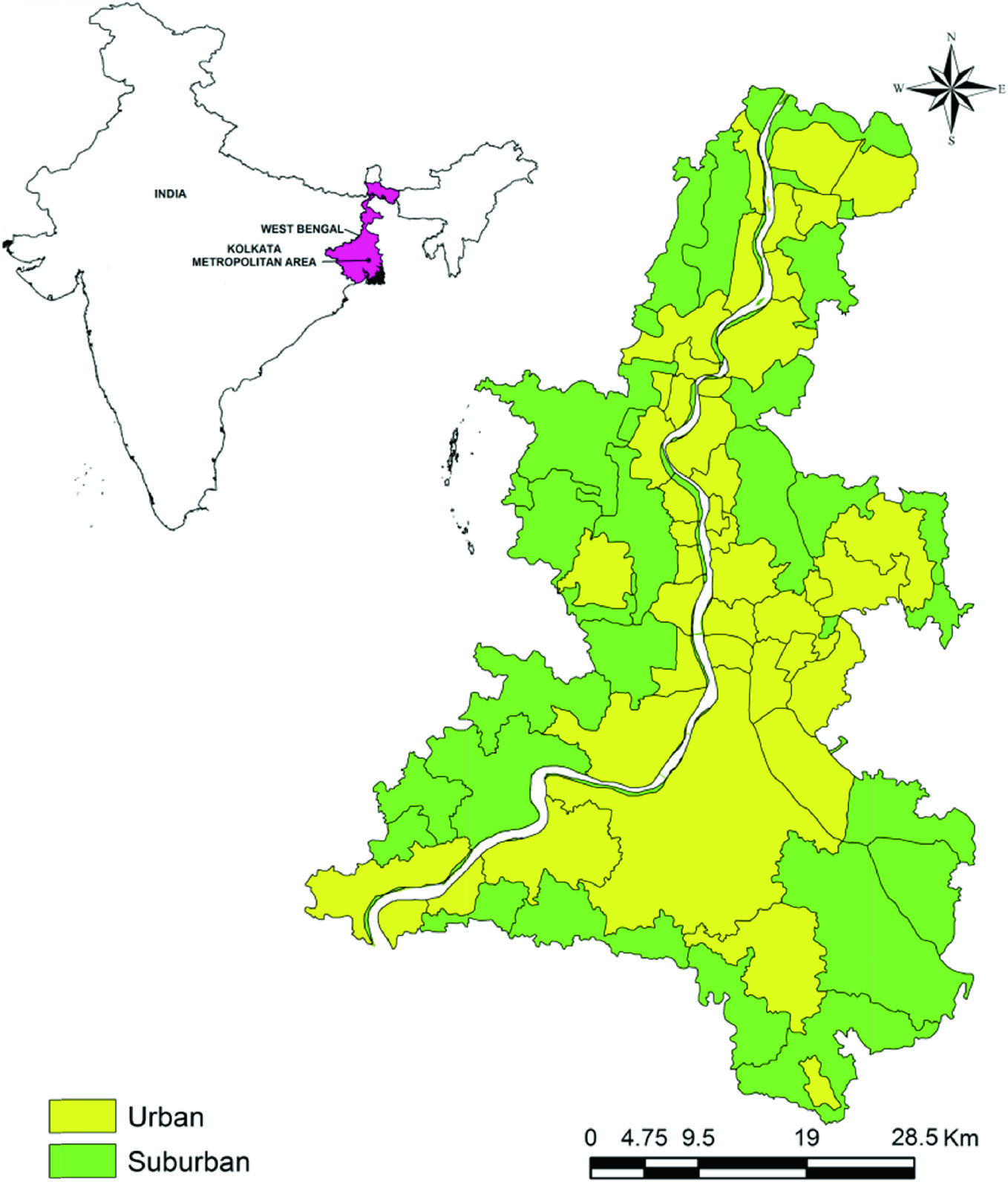
Urban heat island cool roofs remote sensing. The objective of this research is to review the state of knowledge and current research to quantify surface urban heat islands suhi and surface urban cool islands suci. Highlights chicago increased its albedo and ndvi from 1995 to 2008 to combat its urban heat island. Albedo increases were more effective at. To study the uhi effect in the indian context the nagpur urban area has been explored in this paper using landsat 7 etm satellite images through remote sensing and gis techniques.
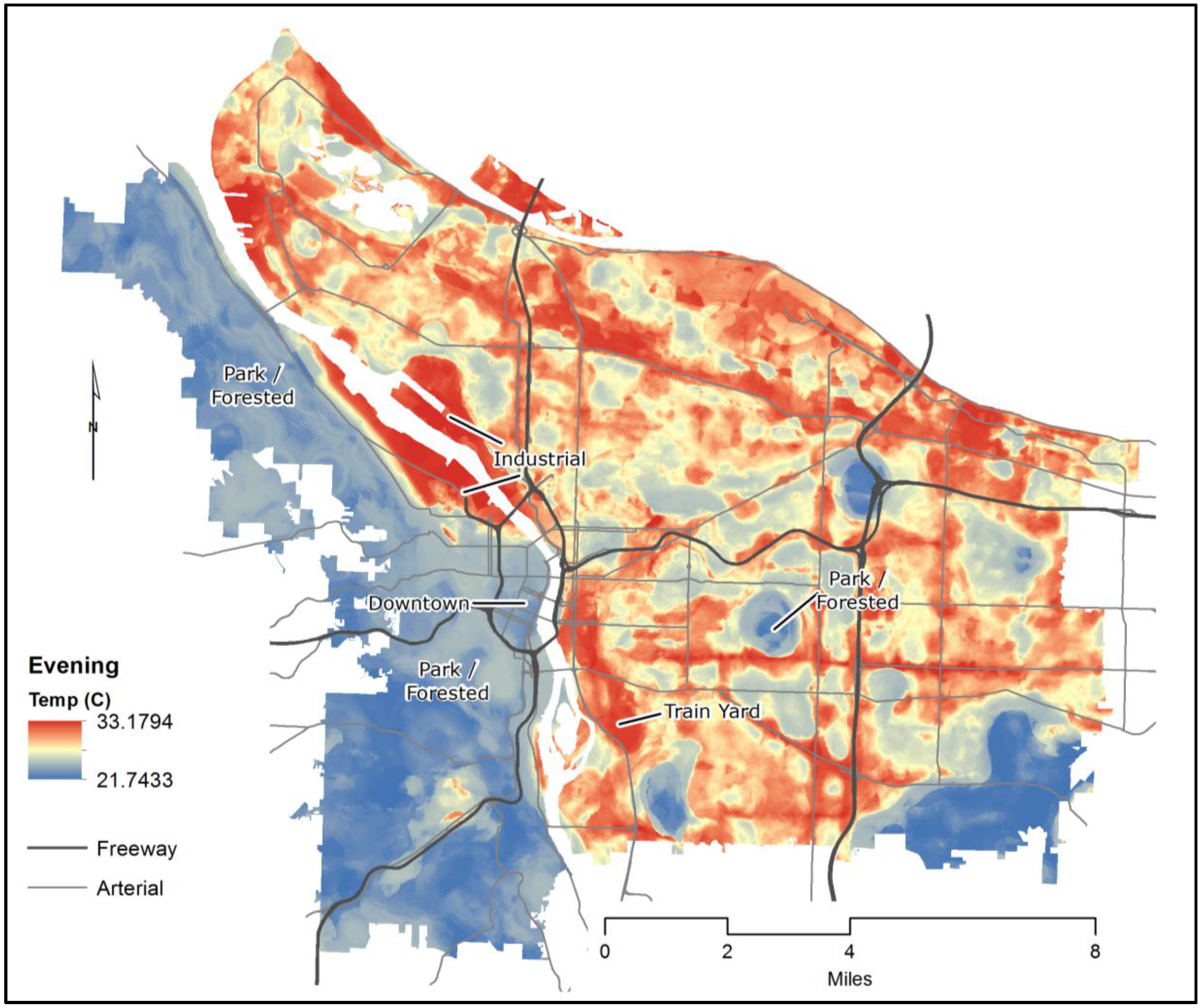
Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect across biomes in the continental usa marc imhoff nasa earth resource technology et al we find that ecological context significantly influences the amplitude of summer daytime uhi urban rural temperature difference the largest 8 c average observed for cities built in biomes dominated by temperate broadleaf and mixed forest. Urban heat island remote sensing modis land surface temperature biomes landsat impervious surface area impervious surface area isa from the landsat tm based nlcd 2001 dataset and land surface temperature lst from modis averaged over three annual cycles 2003 2005 are used in a spatial analysis to assess the. Albedo increases from 1995 to 2008 are strongly correlated to temperature 0 33. Ndvi increases from 1995 to 2008 are weakly correlated to temperature 0 17.
Chicago s albedo increased by 0 016 from 1995 to 2008 while ndvi increased by 0 007. Urban heat island uhi is found more pronounced as a prominent urban environmental concern in developing cities. Using ground based and satellite remote sensing data we present a method to quantify the spatial pattern and diurnal and seasonal variations in canopy layer heat islands clhis in china s 32 major cities during 2009 and investigate their relationships with built up intensity bi nighttime lights vegetation activity surface albedo and surface urban heat island intensity suhii.